Antibiotics in Milk
Photo is illustrative in nature. From open sources.
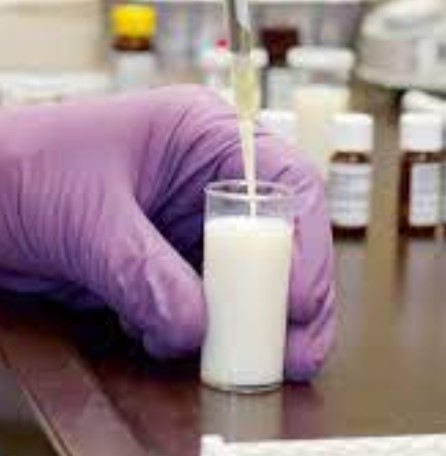
Milk , as one of the key food products, plays an important role in the human diet. Recently, discussions around the antibiotic content of milk have become the subject of increased attention. In this article, we look at how antibiotics can get into milk , what risks this poses, and how the industry is combating this problem.
1. Use of antibiotics in agriculture:
One of the main sources of antibiotics in milk is their widespread use in agriculture. Antibiotics are used to treat and prevent diseases in livestock, and their use is becoming an integral part of modern veterinary practices.
2. Risk of developing antimicrobial resistance:
One of the main concerns associated with the use of antibiotics in livestock is the risk of developing antimicrobial resistance. If animals are given antibiotics in the wrong doses or undertreated, this can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
3. Control measures and standards:
Many countries have strict regulations and controls regarding antibiotic content in milk. Manufacturers are required to ensure compliance with these standards, and products are regularly tested before being placed on the market.
4. Transparency and Labeling:
Transparency regarding the origin of products is becoming a key issue in the food industry. Many producers try to provide consumers with information about whether antibiotics were used in milk production. This may be through labeling or additional information on the packaging.
5. Milk processing technologies:
Milk processing processes such as pasteurization and ultra-pasteurization can affect antibiotic content. The high temperatures used in these processes can destroy some antibiotics, reducing their concentration in the final product.
6. Consumer concerns:
Consumers are increasingly aware of issues related to food safety and food origin. Concerns about the possible content of antibiotics in milk lead to consumers becoming more attentive to the quality of products and demanding of producers.
7. Application of alternative methods in animal husbandry:
Agricultural enterprises are increasingly looking for alternative methods for the prevention and treatment of animals, eliminating or reducing the use of antibiotics. This includes the use of probiotics, industrial...
8. Education and awareness:
Consumer education about the use of antibiotics in agriculture, their effects on food, and control practices is becoming an important tool for creating informed and responsible consumers.
9. Research and Innovation:
Agricultural research and innovation plays a key role in finding new technologies and methods that will reduce reliance on antibiotics while maintaining animal health and welfare.
10. The future of agriculture and consumption:
The future of agriculture and food consumption is closely tied to ethics, responsibility and sustainability. Based on current trends, it can be assumed that in the future agriculture will strive to minimize the use of antibiotics and develop safer and more sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
The issue of antibiotic use in milk poses both potential risks and challenges. Transparency, control and education play an important role in creating a safe and responsible food system. The answers to the challenges posed by the use of antibiotics in milk lie in public awareness, technological innovation and a commitment to a sustainable future.